What are the limitations when exporting Power BI to Excel or CSV using PBRS?
As with all things Power BI, there are limitations you should know & consider when you choose to export your Power BI report or visual to Excel or CSV.
These limitations apply to Power BI visuals only.
They do not apply to Paginated Reports in on-premise PBIRS (Power BI Report Server), cloud (Power BI Service) or SSRS reports in SQL Server Reporting Services.
A full description of how to manually export Power BI visuals to Excel or CSV can be found at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/power-bi/consumer/end-user-export.
The limitations in this document are also applicable when automating the export of your Power BI report, visual or matrix to Excel or CSV using PBRS. Here are the key points from the article:
- The maximum number of rows that can be exported from the Power BI service to .csv and Excel is 30,000.
- Export using Underlying data will not work if the data source is an Analysis Services live connection and the version is older than 2016 and the tables in the model do not have a unique key.
- Export using Underlying data will not work if the Show items with no data option is enabled for the visualization being exported.
- When using DirectQuery, the maximum amount of data that can be exported is 16 MB. This may result in exporting less than the maximum number of rows, especially if there are many columns, data that is difficult to compress, and other factors that increase file size and decrease number of rows exported.
- If the visual uses data from more than one data table, and no relationship exists for those tables in the data model, only data for the first table is exported.
- Custom visuals and R visuals, are not currently supported.
- Export data is not available for users outside of your organization who are using a dashboard that has been shared with them.
- In Power BI, a field (column) can be renamed by double-clicking the field and typing a new name. This new name is referred to as an alias. It is possible that a Power BI report can end up with duplicate field names but Excel does not allow duplicates. So when the data is exported to Excel, the field aliases revert to their original field (column) names.
- If there is unicode character in the .csv file, the text in Excel may not display properly. Although, opening it in Notepad will work fine. Examples of unicode characters are currency symbols and foreign words. The workaround for this is to import the csv into Excel, instead of opening the csv directly. To do this:
- Open Excel
- From the Data tab, select Get external data > From text.
- Power BI admins have the ability to disable the export of data.
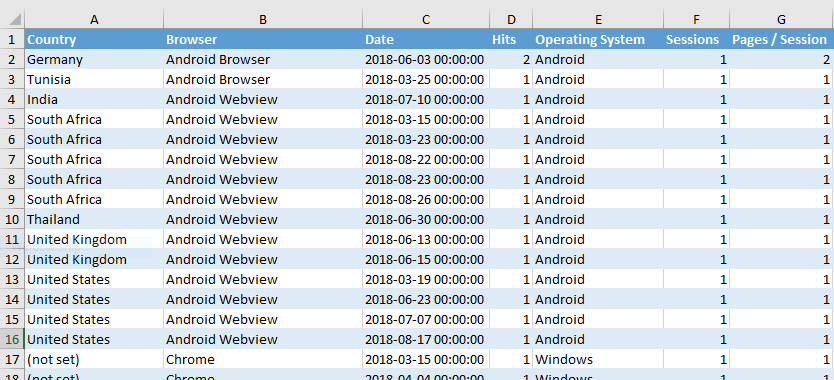
- In order for PBRS to see a Visual (for exporting to CSV or Excel), the Visual MUST have a title.
Learn More about PBRS:
Get Features PDF Start Free Trial