How do I use Data-Driven Package Schedules for Power BI Service Reports & Dashboards in PBRS?
Unlike a Data Driven Schedule, a Data Driven Package will determine the data driver further into the schedule. A Data-Driven Package allows you to send a package of reports to an individual or group from one schedule.
This article applies to:
- Power BI Reports & Dashboards (Cloud - Power BI Service)
Data-Driven Package Report Schedule for Power BI Service Reports & Dashboards.
Unlike a Data-Driven Schedule, a Data-Driven Package will determine the data driver further into the schedule. A Data-Driven Package allows you to send a package of reports to an individual or group from one schedule. In this section, we will define the general properties of the package.
How to Create a Data-Driven Package Schedule Report for Power BI Service Reports & Dashboards?
- Go to Data-Driven Package.
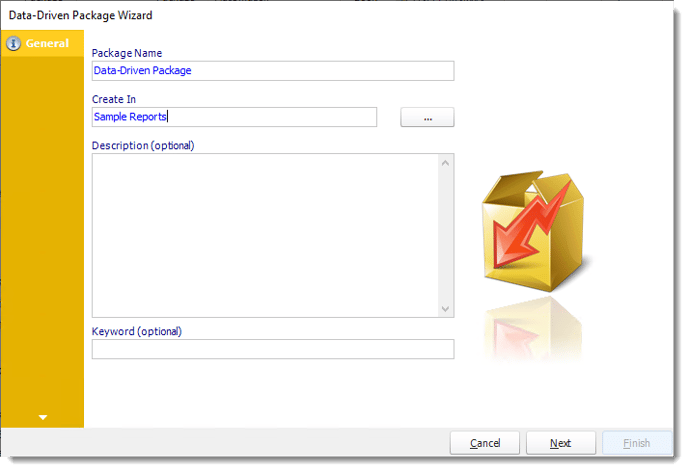
General Wizard
- Package Name: The name of the package.
- Create In: The PBRS folder where the package is stored.
- Description: A short description to help other users identify exactly what this schedule is and what it is expected to do.
- Keyword: Enter some keywords which can be used later by Smart Folders to identify this schedule.
Click Next to continue to the next wizard section.
Schedule Wizard
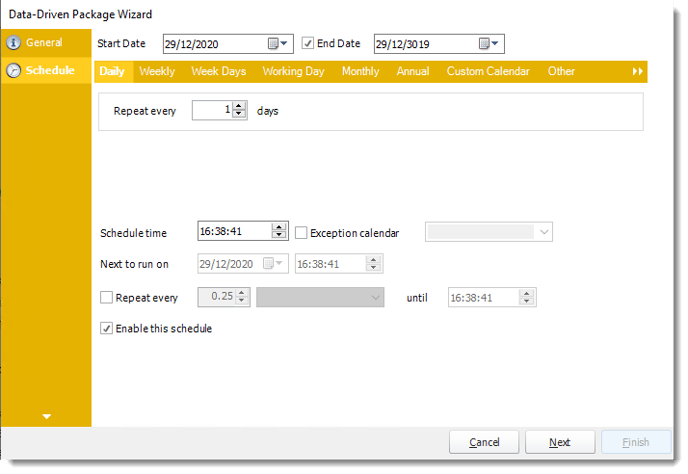
In this section, you will decide when the report will execute. There are a variety of options:
- Daily: Run a report every day or at a frequency of days.
- Sub options: Repeat every X Days.
Example: Run the schedule every 3 days.

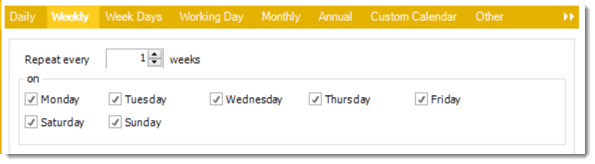
- Weekly: Run a report on a weekly time frame.
- Sub options: Repeat every X weeks.
Example: Run the schedule every 2 Weeks.
- On: Select the specific days of the week the schedule will run. If only once a week, select only the day of the week it will run.
Example: Run every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday.
- Week Days: Run the schedule Monday through Friday.

- Working Day: Run the schedule starting on a specific day of the month. Indicate which day of the month the schedule will run. E.G. run the schedule on the 4th working day of the month.

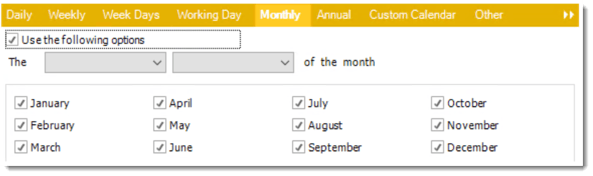
- Monthly: Run the schedule on a monthly time frame.
- Use the following options: Checking this box will enable you to select frequency options such as the “last Thursday of the month.” Also you can include or exclude specific months from the schedule.
- Annual: Run the schedule every year at a specified time.

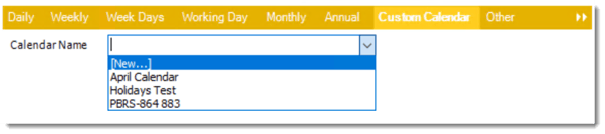
- Custom Calendar: Select the custom Calendar you wish to use. You can create a new custom calendar from the menu as well. Please see Custom Calendars for more information.
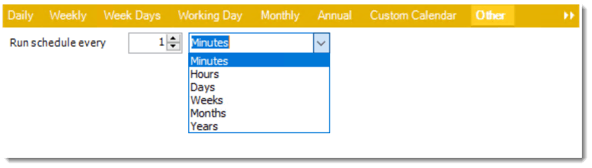
- Other: Other scheduling options.
- Run Schedule every X Minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, years.
- None: No scheduling is required for this item.

- Start Date: Enter the desired starting date for the schedule. This section can be the current date (providing schedule time has not already passed) or a date in the future.
- End Date: If the schedule is due to end after a certain date enter that here. If the schedule is to run indefinitely, then leave it blank.
- Schedule time: On the Next Run date, the package will run at this time.
- Exception Calendar: Choose a calendar that will instruct the schedule to NOT run on those specified days. Please see Custom Calendars for more information.
- Next to run on: The package will next run on this date.
- Repeat Every: Rerun the package every x minutes from the scheduled time until your specified time.
For example, you can set up a daily package to run every day at 8 am, and to run every hour until 5 pm.
- Until: After this date, there will be no automated scheduling of this package.
- Enable this Schedule: Uncheck this option to Disable the package. Disabled packages are not deleted, but they do not execute automatically. You can re-start the automatic scheduling at a later date by checking this option again. Or right-clicking this schedule from the main screen and selecting Enable.
Click Next to continue to the next wizard section.
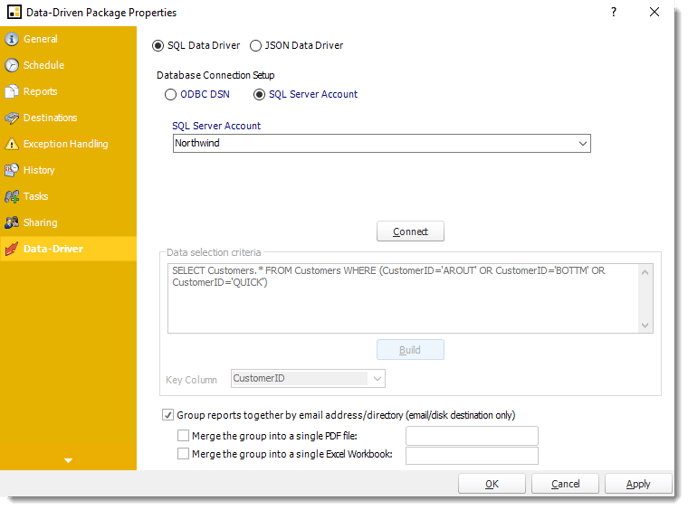
Building a Data Driver Wizard
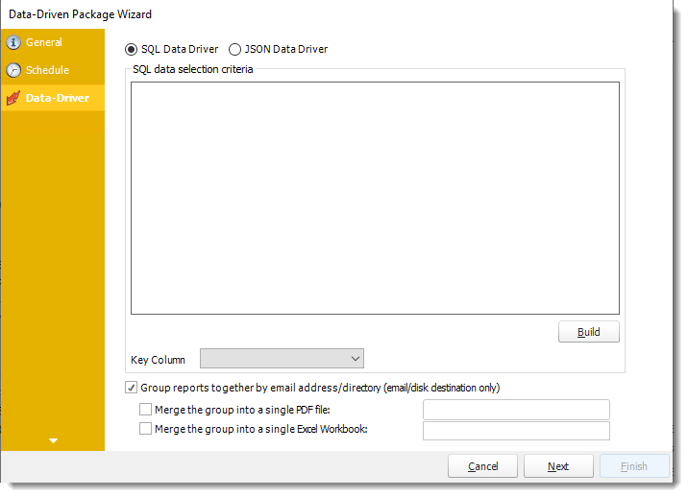
- The Data Driver is where you set up the source for data for your data-driven reports. If your data source or data selection criteria changes this is where you will need to make any required changes. You can either select SQL Data Driver or JSON Data Driver.
SQL Data Driver
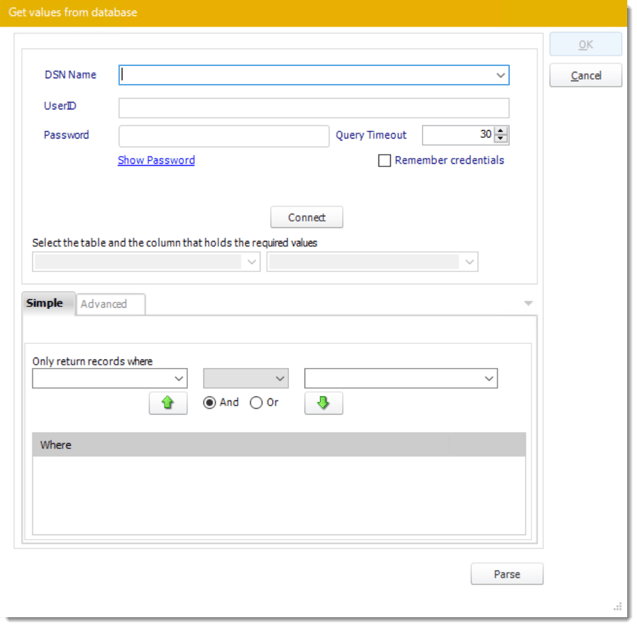
- ODBC Datasource Name: Check this option for ODBC DSN. Drop down and select a DSN.
We strongly recommend System DSNs so that the DSN is visible to PBRS even when the user associated with the DSN is logged off.
All communication to databases (including Access databases) is done through ODBC, so you must setup a system DSN to the database before you can use this facility.
When setting up DSNs we recommend (if possible) that you use Windows Authentication (Trusted Connection). This ensures that your username and password are not required to be stored in PBRS (more secure) and overcomes a large number of security restrictions which Windows places on DSNs. When using Windows Authentication, make sure that the PBRS NT service user (or background application service user) has full rights to the database otherwise, though you will connect when you are logged in, automated scheduling will fail if the Service user has not got rights to the database.
When setting up a DSN to a SQL server, you must ensure that the "Default Database" setting is set to the database you are connecting to (Windows defaults this to "Master").
- UserID: Enter the User ID PBRS should use to log on to the database.
- Password: Enter the password associated with the above user.
- SQL Server Account: Check this option to use your SQL Server Account.
You must add the SQL Server Account in Integrations.
- Connect: Click Connect to connect to the Database.
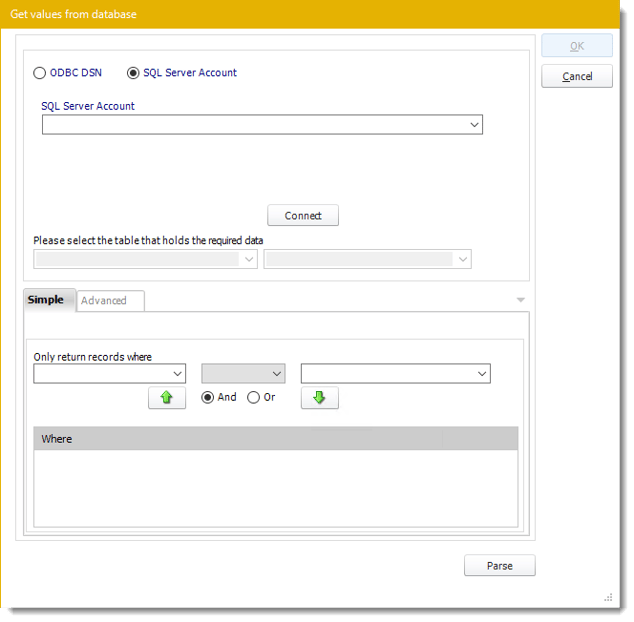
- Select the table from the database that holds the required data. You can refine your selection query by using the simple or advanced tabs.
- Click Parse.
- For more information of "Get Values From Database" interface, click here.
- Click OK.
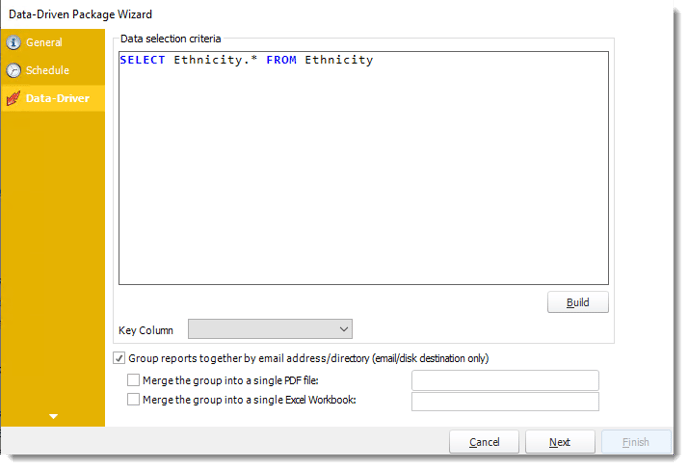
- Click Build to specify the data selection criteria. This will return you to the Build Data Driver tool.
- Key Column: Select the key column for the data that is returned for the reports. The information that drives the schedule is required to have a key column so that each row in the table is uniquely identified by the value in this column. The key column is there as an identifier which is used to troubleshoot in cases where there is a problem with one of the records.
JSON Data Driver
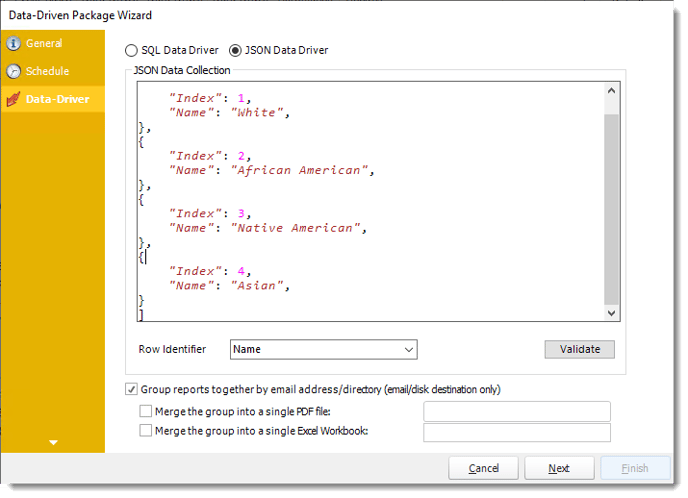
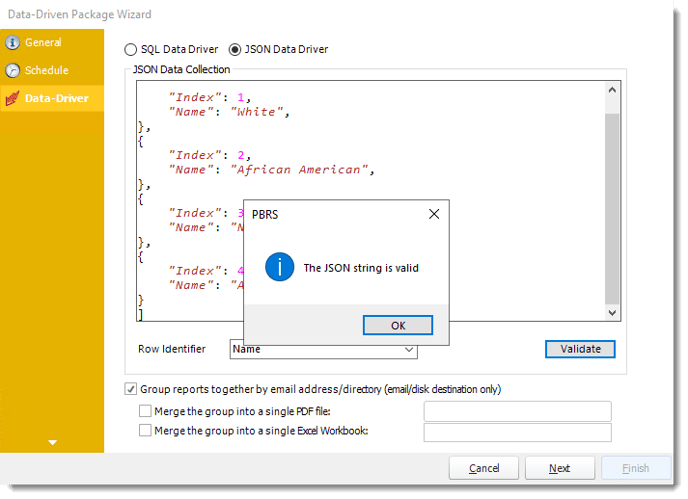
- Enter your JSON string and click Validate.
- Row Identifier: Select the row identifier for the data collection for the reports. The information that drives the schedule is required to have a row identifier so that each row in the table is uniquely identified by the value in this column. The row identifier is there as an identifier that is used to troubleshoot in cases where there is a problem with one of the collections.
- Group reports by email address: You can instruct PBRS to group reports that are sent to the same email address. Please note that enabling this option disables the ability to embed the reports in the email body for email destinations.
- Merging Multiple Reports: Where the reports are grouped you can also instruct PBRS to optionally merge the output of the grouped reports into a single file (PDF and MS Excel formats only). Selecting each option will bring up the options for the output format that you can further customize.
Destination Wizard
In this section, you will decide where your schedule will be delivered. The list in the center will display the list of destinations you have added to the schedule. You can organize the various destinations’ order by clicking on the green up and down arrows.
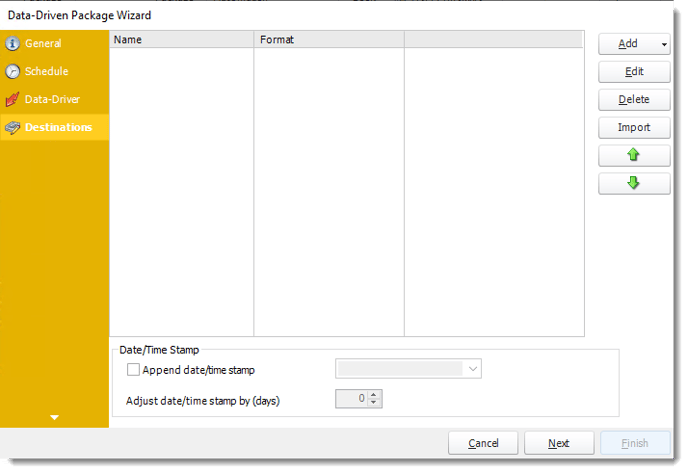
- Add: Click here to add a destination. You have several options which are: Email, Disk, Fax, FTP, ODBC, Printer, Sharepoint, SMS, and Dropbox.
- For more information of adding destinations, click here.
- For more information about Output Formats, click here.

- Edit: Select a destination and click to edit it's properties. Or simply double-click on the destination.
- Delete: Select a destination and click this button to delete it.
- Import: Click here to import from the list of default destinations.
Customizing the Destination
With the Data-Driven Schedule, you can determine the delivery method of your report based on your data. In your table, specify the delivery method by creating a column for each delivery type (FTP, SharePoint, Email, etc.). For each record specify their email, fax number, and so on.
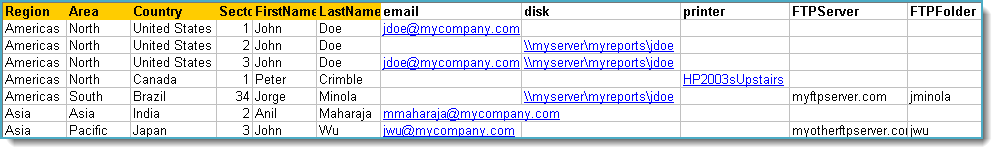
Tip: For email destinations, simply add a semicolon after an email address to send the same instance of the report to another email address.
- Data driving the Report's Distribution
- As mentioned above, PBRS will pull delivery data from your database.
- In this example, we will be using email addresses found in the table.
- With Data-Driven inserts, simply drag and drop the field that indicates your desired destination (email in this case).
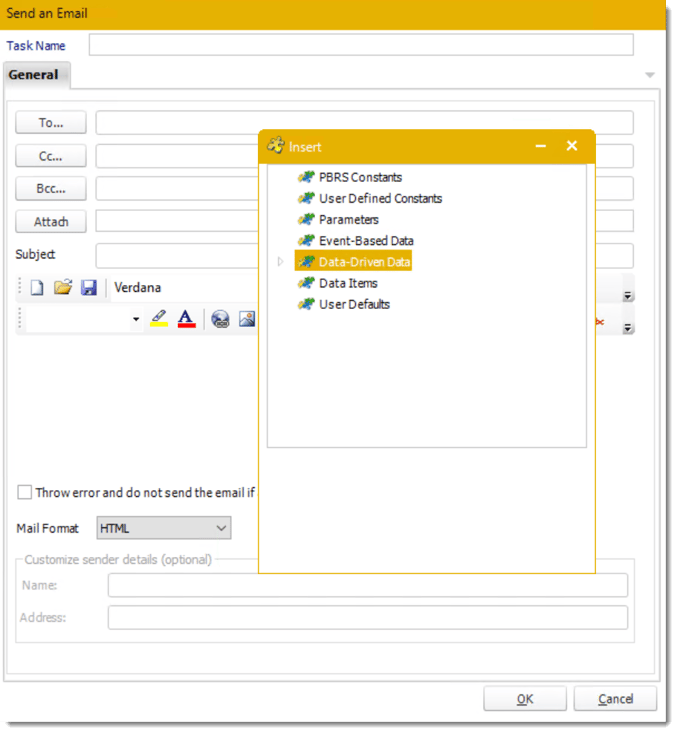
- Now PBRS will deliver a unique report based base on a corresponding email address.
Customize Recipient Messaging
- You can also customize the messaging the recipient receives. Using Data-Driven Inserts, PBRS will automatically pull data from your table and use it to customize the subject, body or report format.
- Simply drag and drop fields from your table to the desired position.
For example, to customize an email greeting, type the greeting, and add the recipient's name as shown above.
Click Next to continue to the next wizard section.
Reports Wizard
A package may be created with no constituent reports and then the reports can be added later. However, you may also add reports at this stage in the wizard - and amend, delete or add some more later.
- Merge all Excel Files: PBRS will then merge all excel outputs in the package into a single excel file.
HINT: Add Password Protection to this section in this option window rather than the individual report in the package. This will password protect the entire merged workbook.
- Merge all PDF Files: Merge PDF outputs into a single PDF file. The reports will appear in the merged PDF in the order they are displayed in the package schedule. Checking this box will bring up additional PDF Options.
- Click Add and go For Power BI and select Reports & Dashboards.
- Package Report Properties will appear on.
Package Report Properties
Report Wizard
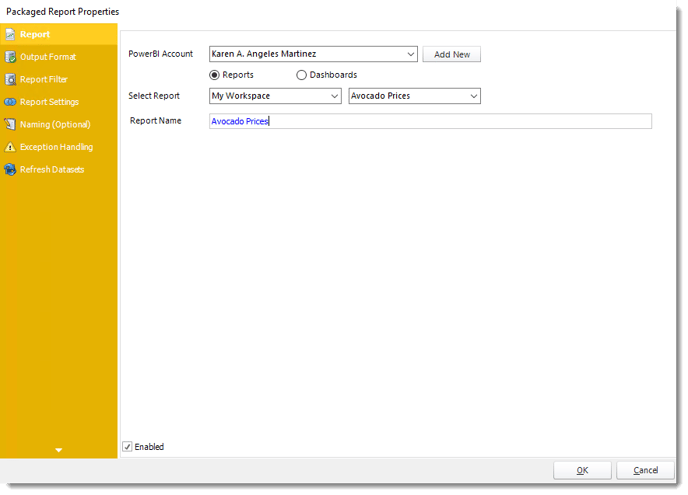
- Power BI Account: Add the account to send the report.
- Select Report: The path to the required report.
- Report Name: Enter a name for the report.
- Enabled: Enable or Disable this specific report in the Package.
Output Format Wizard
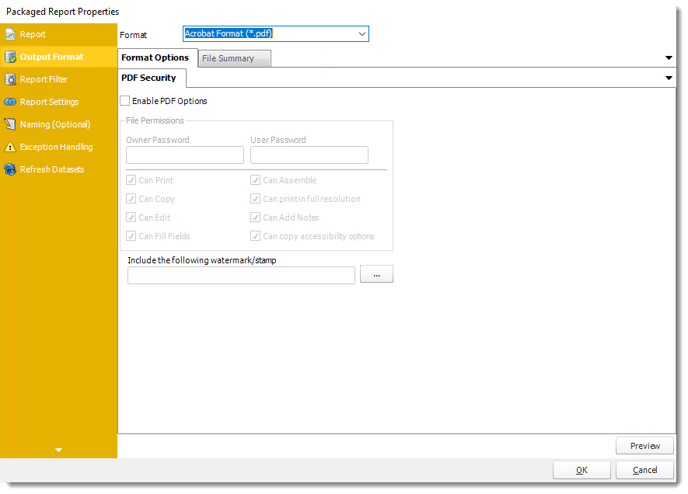
- In this section, you will select the output format of the report.
- For more information on Output Format, click here.
Report Filter Wizard
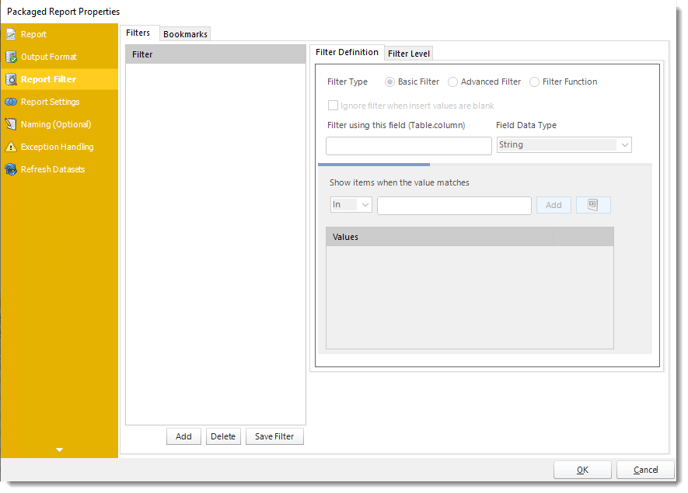
- In this section, you will determine the filters for your report (if any). If your report has no filters, you may skip this section by clicking next.
- With PBRS, you can Data Drive any filter in your report. Ensure the filter values for each record are listed in your database.
- Using Data-Driven Inserts you can pull these values into your report.
- Drag and drop your Data-Driven inserts into the desired filter fields. If you do not wish to enter a data-driven value in your filter, you can still manually type a value or select them from the drop-down box.
- You can also use Inserts Constants to filter the table and column.
Filters
Filters Definition
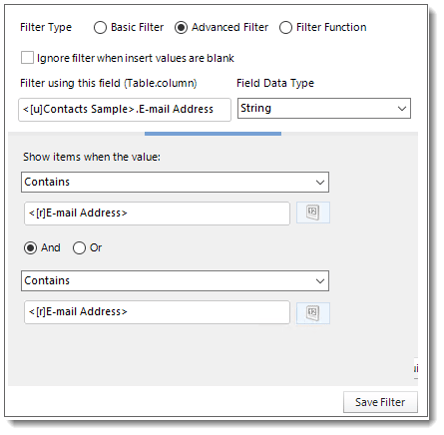
- Filter Type: You may choose between Basic Filter, Advanced Filter, or Filter Function.
- Ignore filter when insert values are blank: Check this option when the filter values are blank.
- Preview: View the dashboard/report output given the selected filters.
- Filter using this field (Table.column): Choose the table and column you would like to set up the filter.
Basic Filter
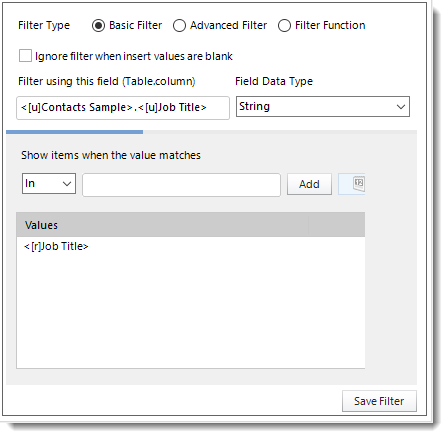
- Click Add.
- Enter the Table.Column names in Filter using this field textbox.
- Select the Field Data Type.
- Select an operator in Show items when the value matches.
- Show items when the value matches: Insert the value you would like to add and then click Add.
- Click Save Filter.
Advanced Filter
- Click Add.
- Select Advanced Filter.
- Enter the Table.Column names in Filter using this field textbox.
- Select the Field Data Type.
- Show Items when the value: In this option, you have the option to show items when the value and select the option from the drop-down menu.
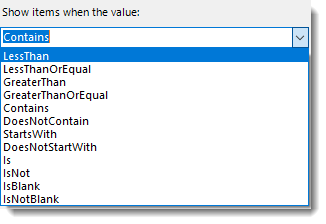
- Click Save Filter to add the filter.
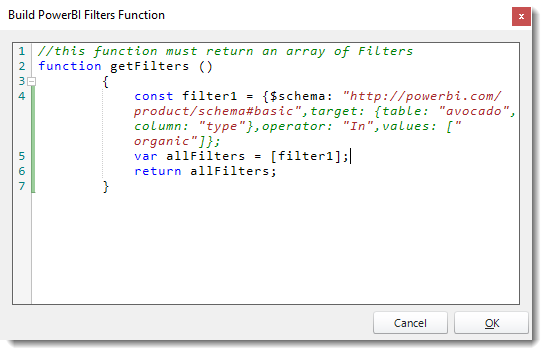
Filter Function
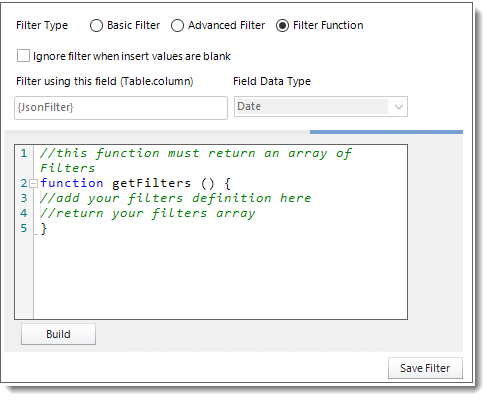
- Select the Filter Function option to enter an advanced Filter JSON string so you don't have to manually configure filters in PBRS.
- Click Build.
- Enter the Filter JSON string.
- Click OK.
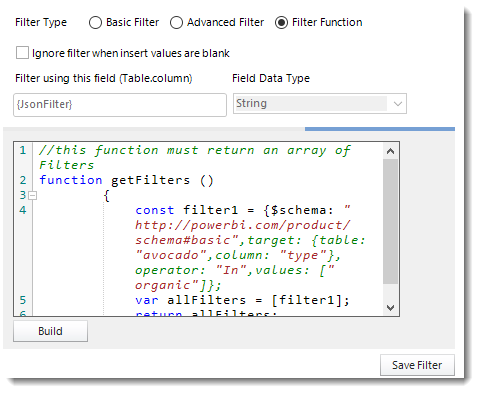
- Click Save Filter.
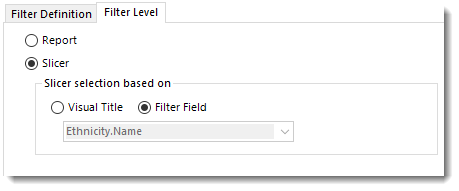
Filter Level
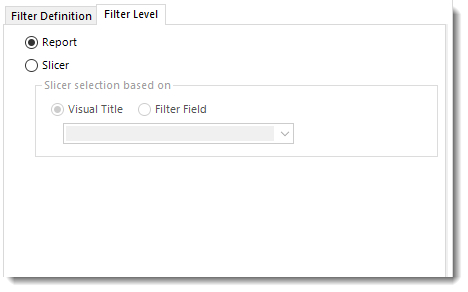
- Report: Check this option to filter the level of the report based on the filter field (Table.Column) value.
- Slicer: Check this option to filter the report based on the slicer visual icon and the filter field value. Using Slicer, all the values of the slicer will be displayed and only the entered value on Filter Field will appear checked.
In order to use the Slicer filter, you must have a Slicer visual in your Power BI Report.
Slicer
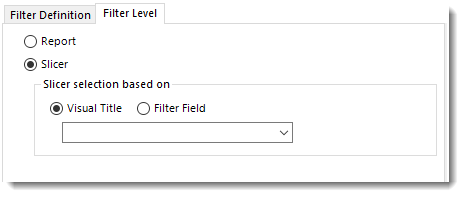
Visual Title
- Visual Title: Using this option, you can select the slicer selection based on the Visual Title of the report. Select the slicer visual title using the drop-down menu.
- Click Save Filter.
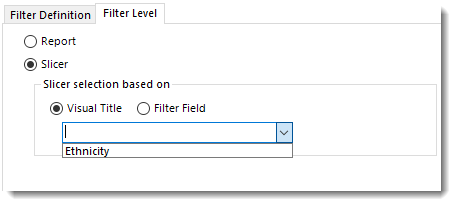
Filter Field
- Filter Field: Using this option, you can select the slicer selection based on the Filter Field (Table.Column).
- Click Save Filter.
Bookmarks
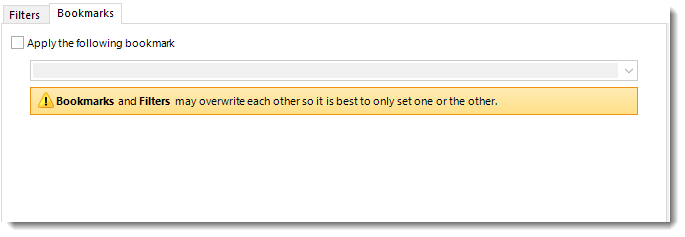
Bookmark and Filters may overwrite each other so it is best to only set one or the other.
- If you have a Bookmark in the report you have the ability to select the bookmark using the drop-down menu.
- Check Apply the following bookmark to enable the Bookmarks option.
- Select the bookmark from the drop-down menu.

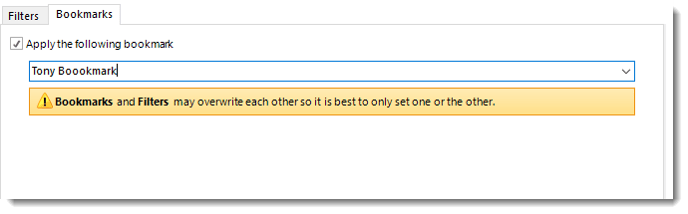
- Click Save Filter to add the filter.
Report Settings Wizard
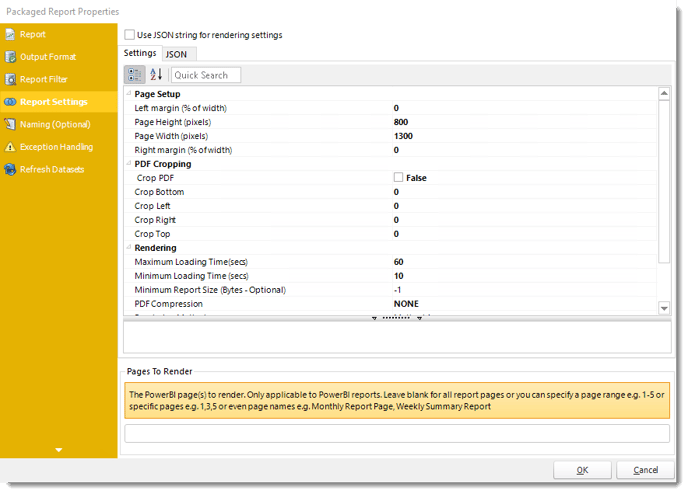
- In this section, you may set up the dashboard/report.
Settings and JSON Rendering settings may overwrite each other so it is best to only set one or the other.
Settings
- Left margin (% of width): The size of the left margin as a percentage of the page width.
- Page Height(pixels): The height of the rendered file.
- Page width (pixels): The width of the rendered file.
- Right margin (% of width): The size of the right margin as a percentage of the page width.
- PDF Cropping: You may crop your reports by page height (pixels) and page width (pixels).
- Maximum Loading Time(secs): The maximum amount of time that the renderer will wait before timing out.
- Minimum Loading Time(secs): The amount of time that PBRS will wait for the dashboard/report to load before rendering it to file.
- PDF Compression: Select PDF compression levels.
- Rendering Method: Select the rendering method type for your Power BI report.
- Transparent Background: You have the option to have your Power BI report in a transparent background.
- View Style: How the report fits on the page: Fit to Page, Fit to Width, or Actual Size.
- Page To Render: The Power BI page(s) to render. Only applicable to Power BI reports. Leave blank for all report pages or you can specify a page range e.g 1-5 or specific e.g. 1,3,5. You can enter page names e.g. Monthly Report Page, Weekly Summary Reports.
You can drag and drop Inserts constants into Pages To Render textbox.
JSON
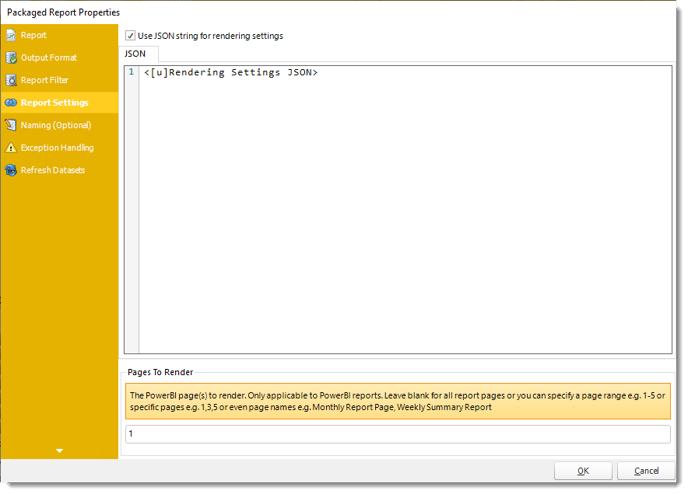
- Use JSON string for rendering settings: Check this option to use JSON string for the rendering settings.
- Enter the JSON string.
You can drag and drop Inserts constants into JSON textbox.
Naming (Optional)
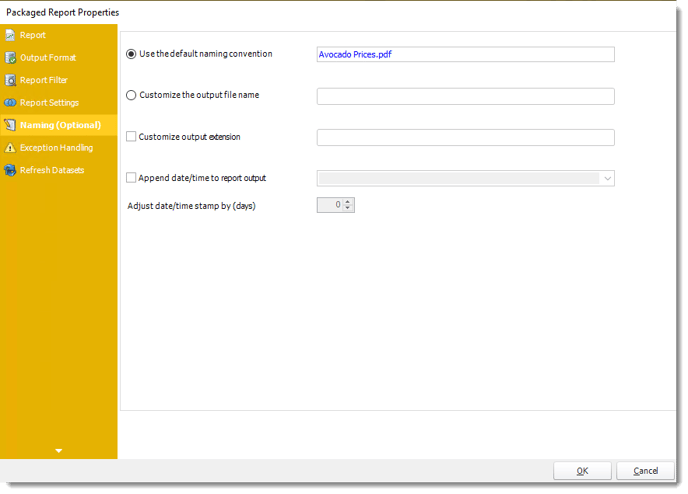
- Default Naming Convention: PBRS will name the output file in the following format: reportname.format extension, e.g. Catalog Report.pdf.
- Customize the output file name: Choose your own filename or right-click and use the Insert Function to insert a value.
- Customize output extension: Choose your own extension. This is useful for system integration. For example, the default extension for a character separated file is "CSV," but you can give your export an extension of "txt" so that the file can be read by another already existing system you may have. You may also right-click and use the Insert Function to insert a value.
- Append date/time: This is useful for the following reasons:
- If the filename is the same each time, and it is being exported to the same folder each time, then it will be overwritten by the latest one each time. By appending date and time to the filename, each file remains unique, and no files are overwritten.
- You can track which reports ran and when they ran by looking at what the report is named.
Exception Handling Wizard
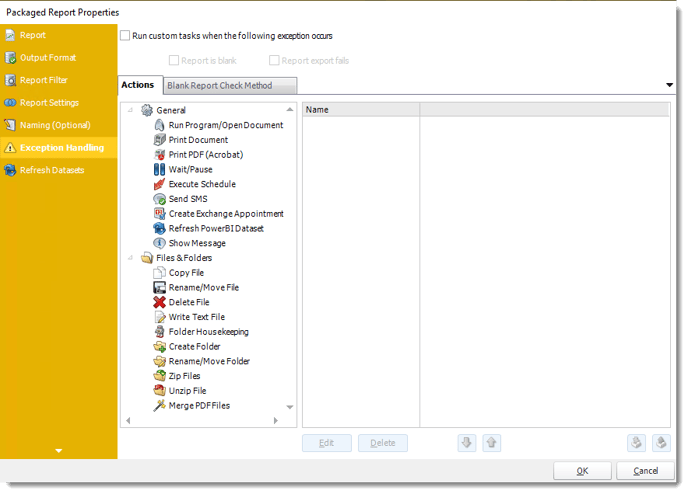
- Run custom tasks when the following exception occurs: Check this is option to enable the following options.
-
- Report is Blank: If a report is blank because it genuinely returned no data, recipients can misconstrue this as an error with the scheduler. This option allows you to identify genuine empty reports and instruct PBRS on what to do with them.
- Report exports fail: If a report export fails, you can receive a notification or run a tasks that the report failed to execute.
- Ignore the report and subsequent tasks: If the report is blank, do not send the report. The report will not be delivered to the destination. No custom tasks will be run.
Actions
- Select an action from the task list. This task will be executed in the event that a schedule is blank.
- For more information about tasks, click here.
You can send a notification if a report is considered blank instead of sending the report. Simply select “check if a report is blank” then select “Ignore the report.” In the actions tab, select “Send Email” from the list. Compose your email and save.
Blank Report Check Method
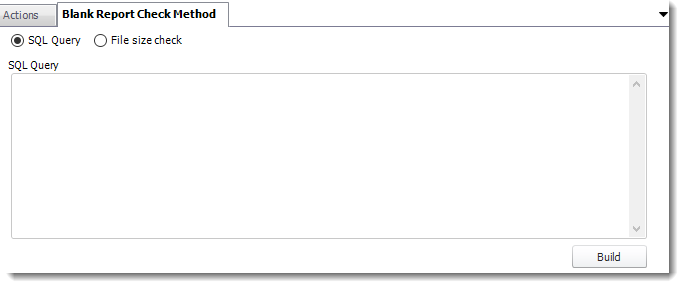
- Select the Method that will determine whether a report is blank.
- SQL Query: Select this option to use a user made query that will determine if the report is blank. If the query returns no results, the report is blank.
- Click Build.
- Get values from a database window will appear. For more information about Get values from database, click here.
- File size check: Assume reports is blank if size is under "X" bytes.
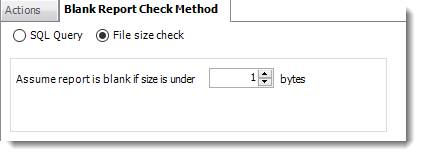
- Click OK.
Refresh Datasets
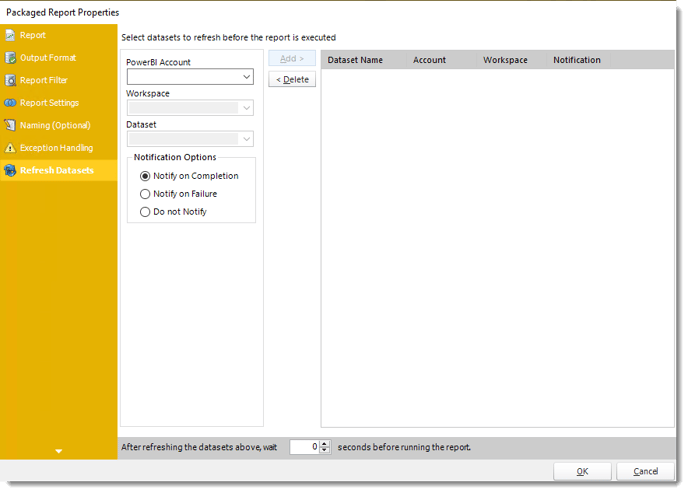
In this section select the datasets to refresh before the report is executed.
- Power BI Account: Select the account to refresh datasets.
- Workspace: The path to the required report.
- Dataset: Select the dataset.
- Notification Options: Receive a notification after the report is executed, the report failed to execute, or do not receive a notification.
- After refreshing the datasets above, wait 'X' seconds before running the report.
Exception Handling Wizard
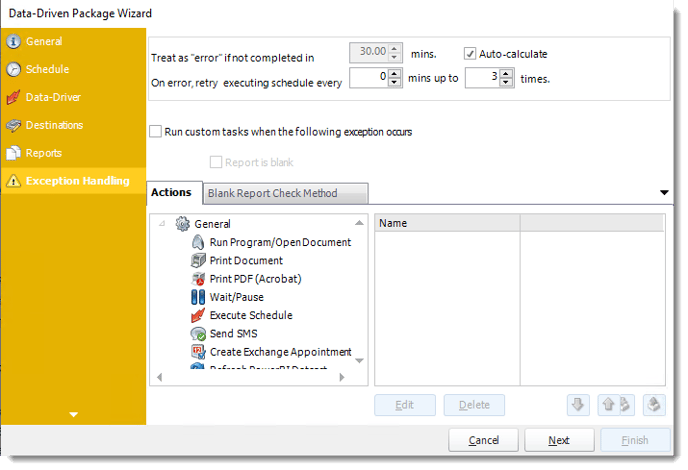
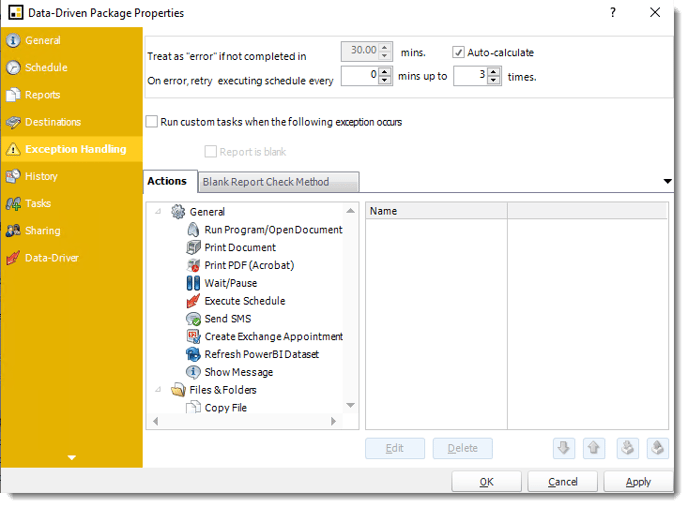
- Treat as “error” if not completed in X minutes: If a report takes longer than the specified amount of time to run, this option will treat the schedule as an error and follow the appropriate action. The “Auto-calculate” option instructs PBRS to automatically determine how long a schedule should take to run the report. If it takes longer than the calculated amount of time, then it is an error.
If manually determining the error timing, please double-check the run time of the report in order to get the correct time estimate.
- On error, retry executing schedule every: If set to 0, PBRS will deem the schedule as "Failed" the first time it encounters an error. The schedule will not run again until its next scheduled time. Change the value to tell PBRS how many times you want it to retry running the report before declaring it as "Failed."
- Run custom tasks when the following exception occurs: Check this is option to enable the following options.
- Report is Blank: If a report is blank because it genuinely returned no data, recipients can misconstrue this as an error with the scheduler. This option allows you to identify genuine empty reports and instruct PBRS on what to do with them.
- Ignore the report and subsequent tasks: If the report is blank, do not send the report. The report will not be delivered to the destination. No custom tasks will be run.
Actions

- Select an action from the task list. This task will be executed in the event that a schedule is blank.
- For more information about tasks, click here.
You can send a notification if a report is considered blank instead of sending the report. Simply select “check if a report is blank” then select “Ignore the report.” In the actions tab, select “Send Email” from the list. Compose your email and save.
Blank Report Check Method

- Select the Method that will determine whether a report is blank.
- SQL Query: Select this option to use a user made query that will determine if the report is blank. If the query returns no results, the report is blank.
- Click Build.
- Get values from a database window will appear. For more information about Get values from database, click here.

- File size check: Assume reports is blank if size is under "X" bytes.

- Click OK.
Click Next to continue to the next wizard section.
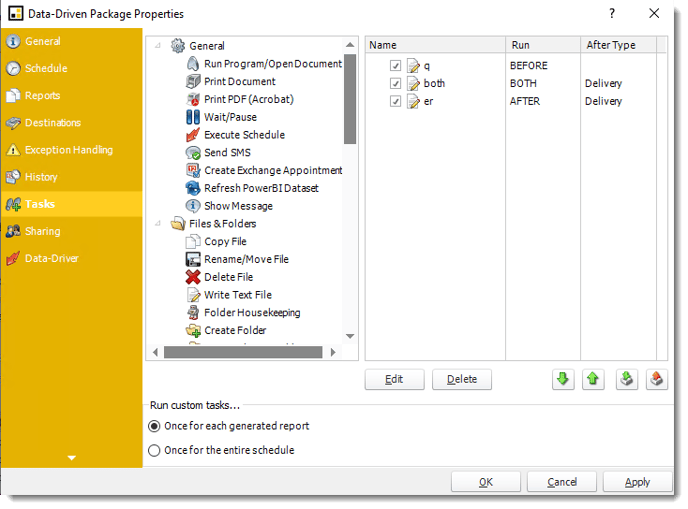
Custom Tasks Wizard
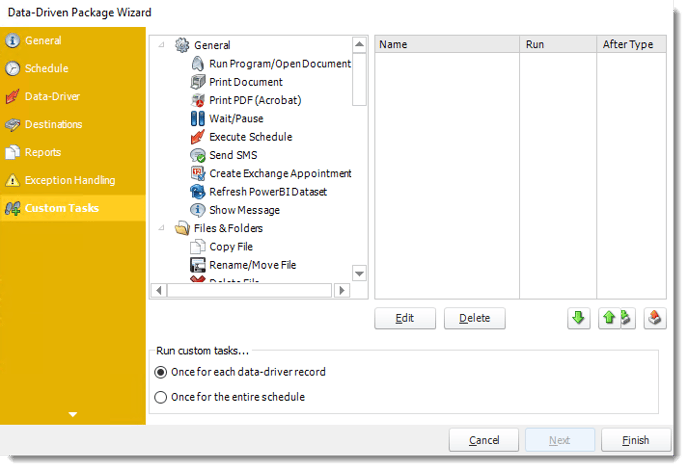
- In the section you have the option of setting up custom tasks. Custom tasks are business process automation tools that can be auto triggered before or after a report runs.
- For more information on Custom Tasks, click here.
- If you have no desire to add a Custom Task, you can click finish to complete the schedule.
Data-Driven Package Report Schedule Context Menu
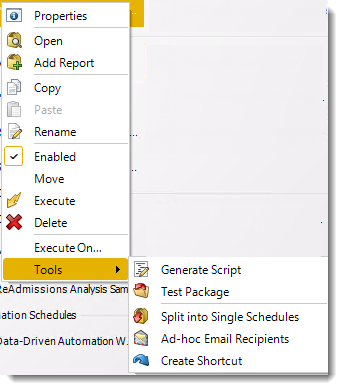
Right-Click on a schedule to see the following actions:
- Properties: Edit the schedule from here. Or you can just double click on the schedule.
- Open: This will open the package and show its constituent reports.
- Add Report: Use this to add one or more reports to an existing package.
- Copy: Use this to copy the schedule. Right-click in the "white space" of the folder you wish to copy it to and select the Paste button.
- Rename: Rename the package.
- Enabled: Schedules are enabled when there is a check icon beside this option. To stop a schedule from running, or to "pause" it for a while, select this option to remove the check icon. Disabled schedules will not run until they are enabled again.
- Move: Use this option to move the report into an existing package.
- Execute: This button will execute the schedule immediately. Note that the next run date and time is not moved on as a result of a manual execution. They only move on if the schedule is run automatically by one of the schedulers .
- Delete: Selecting this option will delete the schedule.
- Execute On: Use to option to execute the schedule to another collaboration server.
- Test Package: Use this option to test the schedule and export it to selected "test" destinations.
- Split into Single Schedules: This will split all the constituent reports in the package into Single Report Schedules.
This process will automatically delete the package once the splitting process is completed.
- Ad-Hoc Email to Recipients: Select this option to send an ad-hoc email to all recipients of this package. You can use this to alert recipients to a planned system outage, or any other useful information.
- Create Shortcut: Use this option to create a shortcut you can save in any location on your PC. Execute the shortcut to execute the schedule in PBRS.
Data-Driven Packages Properties
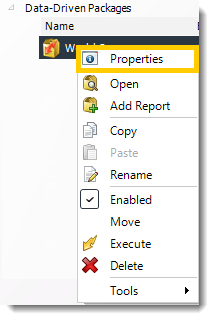
- To access your schedule properties, right click on a schedule and select properties.
- Similar to the schedule wizard, you adjust settings to your schedule such as timing, error handling, or custom tasks.
- General
You can view the Schedule Unique ID in the General Wizard.
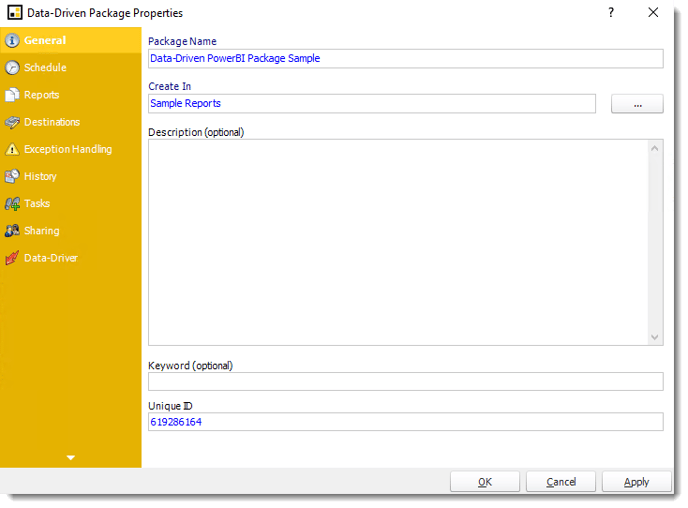
- Schedule
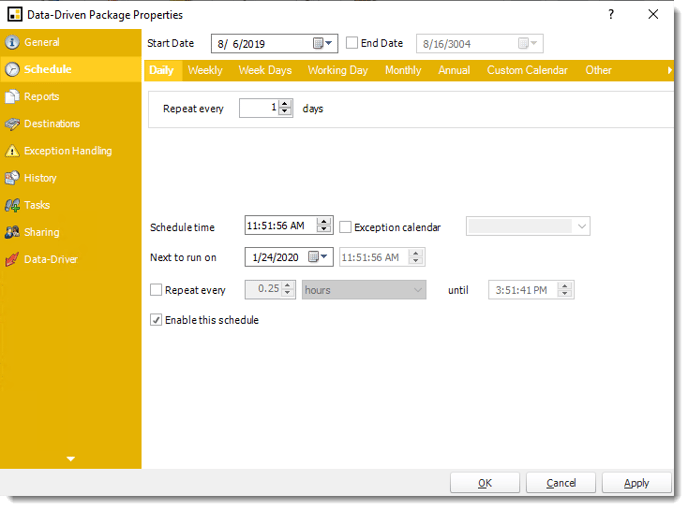
- Reports
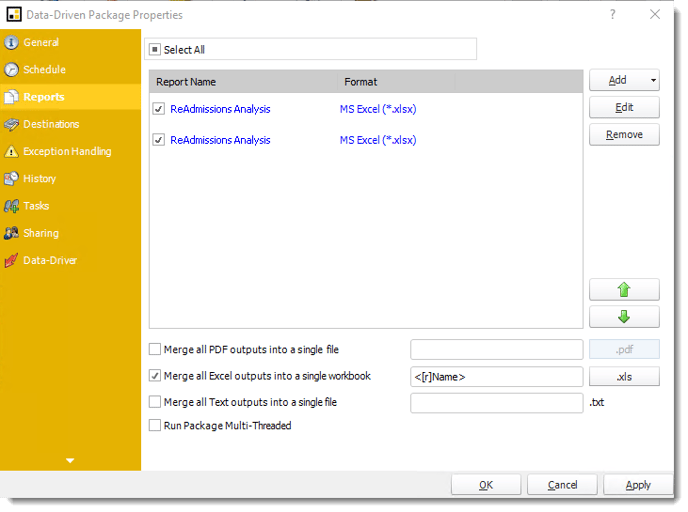
- Destinations
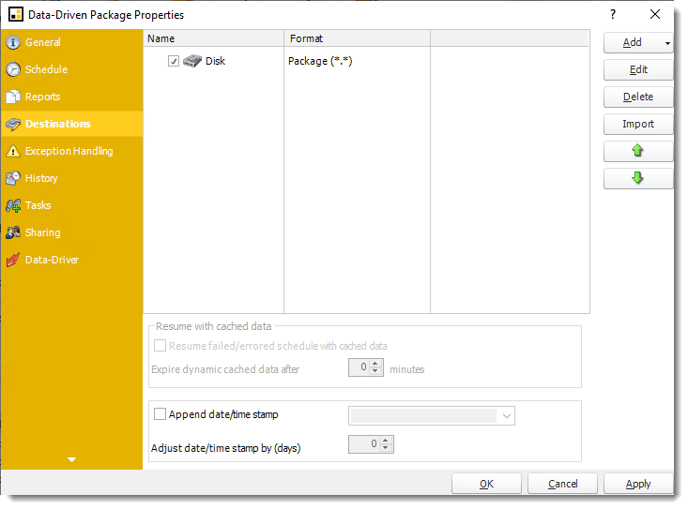
- Exception Handling
- History
- Tasks
- Sharing: Here you can share this schedule with multiple users.
- Data-Driver